Relate Requests to Requests - Overview
Relating Requests to one another increases the Request Administrator's ability to implement ITIL best practices. This feature provides a way to quickly search for and relate like Issues. This is helpful for Root Cause Analysis where a Problem Management team may want to create a Request to log troubleshooting steps taken to resolve an unknown problem while at the same time, having all of the individual incidents, that were likely caused by this problem, only a click away.
There are 2 scenario's (displayed below) that the Request Relation feature will handle.
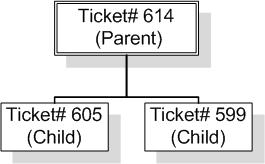
- Parent/Child Relationship - Scenario: An admin user is editing Request number 614. He decides to see if there are any other Requests that may be related or have the same issue. After searching, he finds that Requests 605 and 599 have the same problem. The user relates 605 and 599 as children Requests to 614; the parent Request. See the example below:
- Peer to Peer Relationship - Scenario: An admin user is editing Request number 614. He decides to see if there are any other Requests that may be related or have the same issue. After searching, he finds that Requests 605 and 599 have the same problem. The user relates 605 and 599 as peers to Request 614. See diagram below:

Note: The “Add Related Request” button will not appear on Requests that are a child of another Request. The “Add Related Request” button will appear on Requests that are parents or peers of other Requests.
Sub Articles
 Relate Requests - Parent/Child Relationship
Relate Requests - Parent/Child Relationship
 Relate Requests - Peer to Peer Relationship
Relate Requests - Peer to Peer Relationship